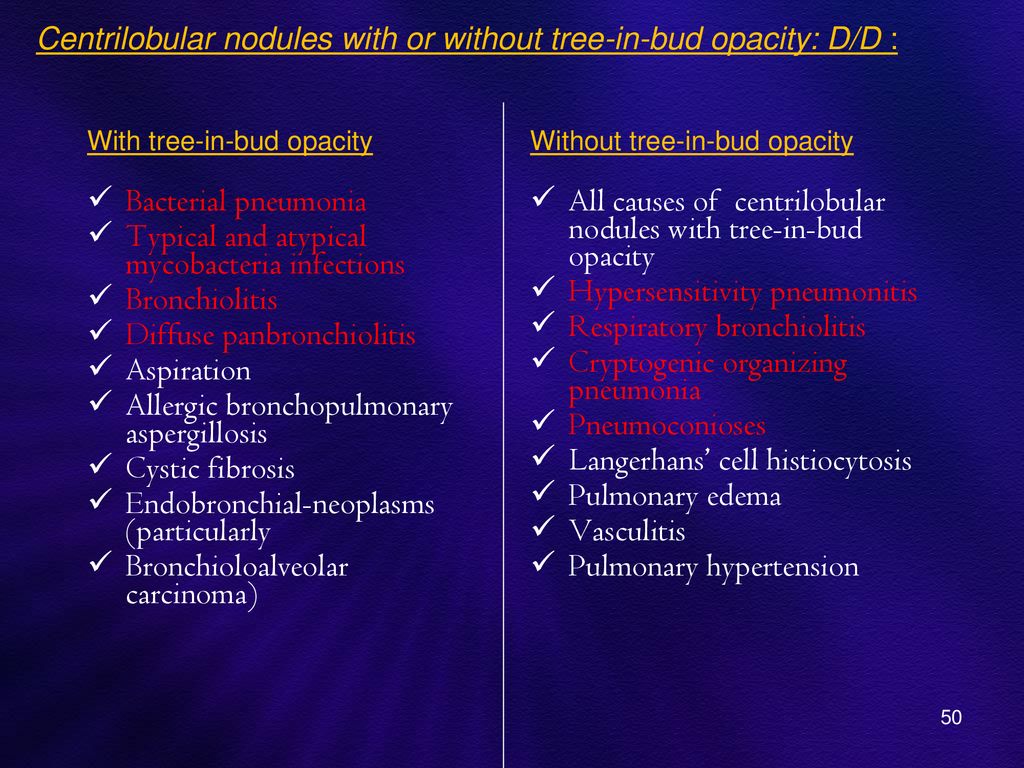
tree in bud opacities causes
The purpose of this study was to. Infective bronchiolitis bacterial pneumonia eg.

Ct Scan Of The Chest Axial View With Tree In Bud Opacities Bilateral Download Scientific Diagram
Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging fi nding on thoracic CT scan.

. Staphylococcus aureus Haemophilus influenzae Mycobact erium tuberculosis Mycobacterium avium MAIC viral pneumonia fungal pneumonia eg. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. The tree-in-bud appearance may occur in case of distal airway diseases in bacterial viral and fungal infections in some congenital diseases for example cystic fibrosis in some idiopathic.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. The main causes of tree-inbud findings in the general population are reported to be acute or chronic infections mainly from nontuberculous mycobacteria and. The main causes of tree-inbud findings in the general population are reported to be acute or chronic infections mainly from nontuberculous mycobacteria and.
The examination shows a nearly uniform distribution of TIB opacities arrows across the lungs bilaterally. Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses four of 166 3 or multiple organisms six of 166 4 were most common. Aspiration was the cause in 42 of 166 25.
The purpose of this. Read customer reviews find best sellers. Diffuse panbronchiolitis is an exudative bronchiolitis.
Tree-in-bud TIB appearance in computed tomography CT chest is most commonly a manifestation of infection. Coronal reconstructed computed tomography image shows the lingular cavity with irregular nodules and right mid-lung nodular opacities in a 43-year-old man who. A young male patient who had a history of fever cough and respiratory distress presented in the emergency department.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. Respiratory infections cause about 72 of cases with 39 due to Mycobacterial cases 27 due to other bacteria and 3 due to viruses. Bronchiectasis which may be of any cause can produce the tree-in-bud pattern.
CT of the chest Figure 2B and 2C performed without the administration of intravenous contrast material revealed multifocal clustered. We here describe an unusual cause of TIB during the COVID-19 pandemic. 3A 3B a condition that develops in approximately 5 of patients with primary infection and is frequently associated with malnutrition and immune suppression.
Aspiration was the cause in 42 of 166 25. Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses four of 166 3 or multiple organisms six of 166 4 were most common. Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. Tree in bud opacities icd 10.
As you can see the possible causes of a tree in bud appearance are legion. These small clustered branching and nodular opacities represent termi- nal airway mucous impaction with adjacent peribron- chiolar inflammation. Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases.
Histopathologic studies have shown that the tree-in-bud pattern is caused by demarcation of the normally invisible branching course of the peripheral airways which usually results from bronchioles being plugged or blocked with mucus pus or fluid. Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses four of 166 3 or multiple organisms six of 166 4 were most common. The tree-in-bud sign has been described in cases of acute aspiration 13.
Aspiration was the cause in 42 of 166 25. 3 found that the tree-in-bud pattern was seen in 256 of the CT scans in patients with bronchiectasis. Where there is small airways disease and tree in bud is present this can be termed an exudative bronchiolitis.
Mycobacterium avium complex is the most common cause in most series. Mycobacterium avium complex is the most common cause in most series. What causes tree in bud opacities.
What causes tree in bud opacities. What causes tree in. Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases.
Where there is small airways disease and tree in bud is present this can be termed an exudative bronchiolitis. In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction. The classic cause of the tree-in-bud pattern is postprimary tuberculosis Fig.
Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. Tree in bud opacities in lungs Sunday May 8 2022 2 However the classic cause of tree-in-bud is Mycobacterium tuberculosis especially when it is active and contagious and associated with cavitary lesions. 1-4Reported causes include infections aspiration and a variety of infl ammatory conditions.
2 However the classic cause of tree-in-bud is Mycobacterium tuberculosis especially when it is active and contagious and associated with cavitary lesions. Simply put the tree-in-bud pattern can be seen. Another important entity that can produce the tree-in-bud pattern is bronchioalveolar carcinoma BAC 1.
87 rows Because any organism that infects the small airways can cause a tree-in-bud pattern. Aspergillus allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis ABPA pneumocystis pneumonia congenital cystic fibrosis. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
Aspiration was the cause in 42 of 166 25. The differential diagnosis of tree-in-bud nodules includes infection and aspiration the two most common causes as well as congenital airway diseases allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis follicular bronchiolitis panbronchiolitis intravenous injection of foreign material and intravascular tumor emboli. Tree-in-bud TIB appearance in computed tomography CT chest is most commonly a manifestation of infection.
Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses four of 166 3 or multiple organisms six of 166 4 were most common.

Ground Glass Opacification Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Ct Scan Of The Chest Axial View With Tree In Bud Opacities Bilateral Download Scientific Diagram
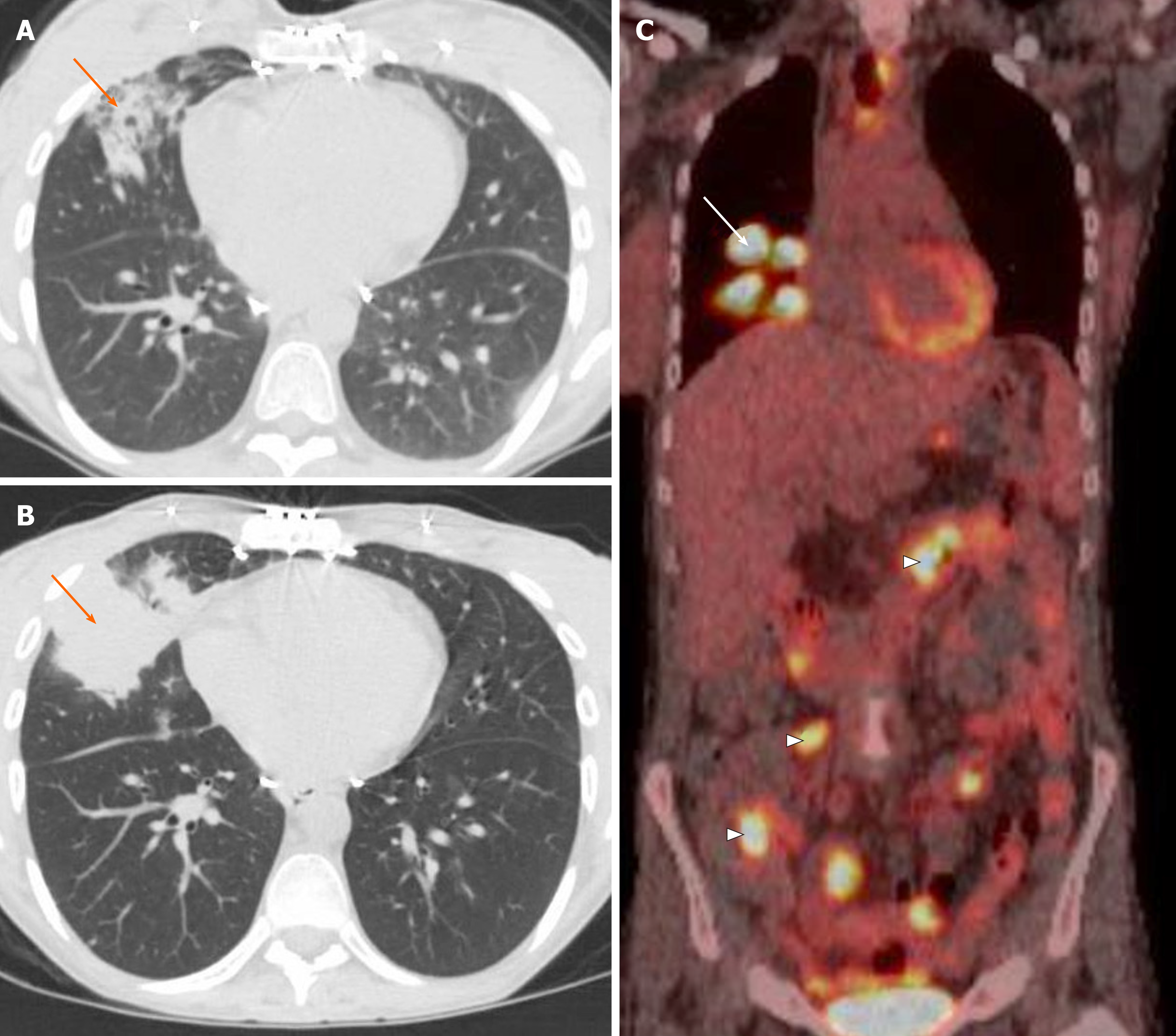
Chronic Airspace Disease Review Of The Causes And Key Computed Tomography Findings

Computed Tomography Scan Showing Disseminated Micronodular Opacities Download Scientific Diagram
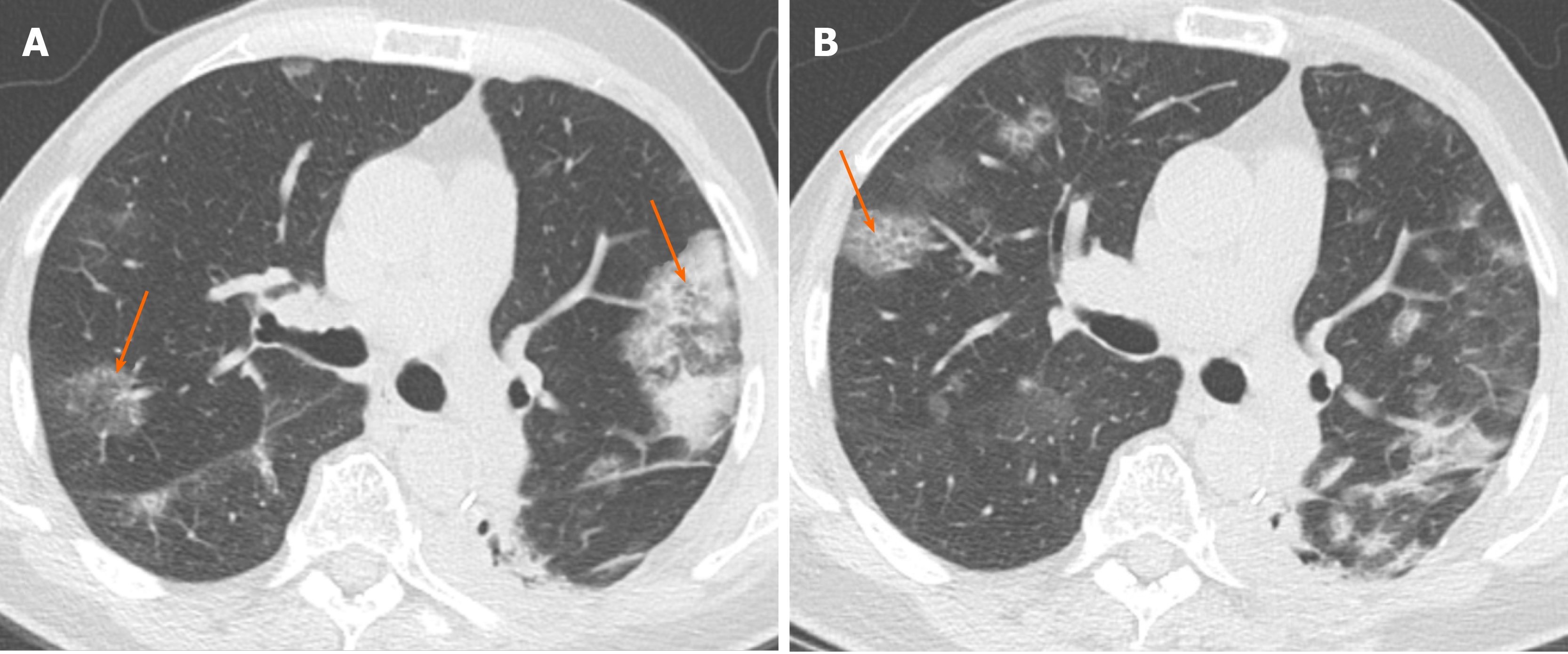
Chronic Airspace Disease Review Of The Causes And Key Computed Tomography Findings

Clinical Characteristics And Ct Manifestations Of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis In Hospitalised Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Clinical Radiology
Technical Aspect Of Hrct Interstitial Lung Diseases Ppt Download
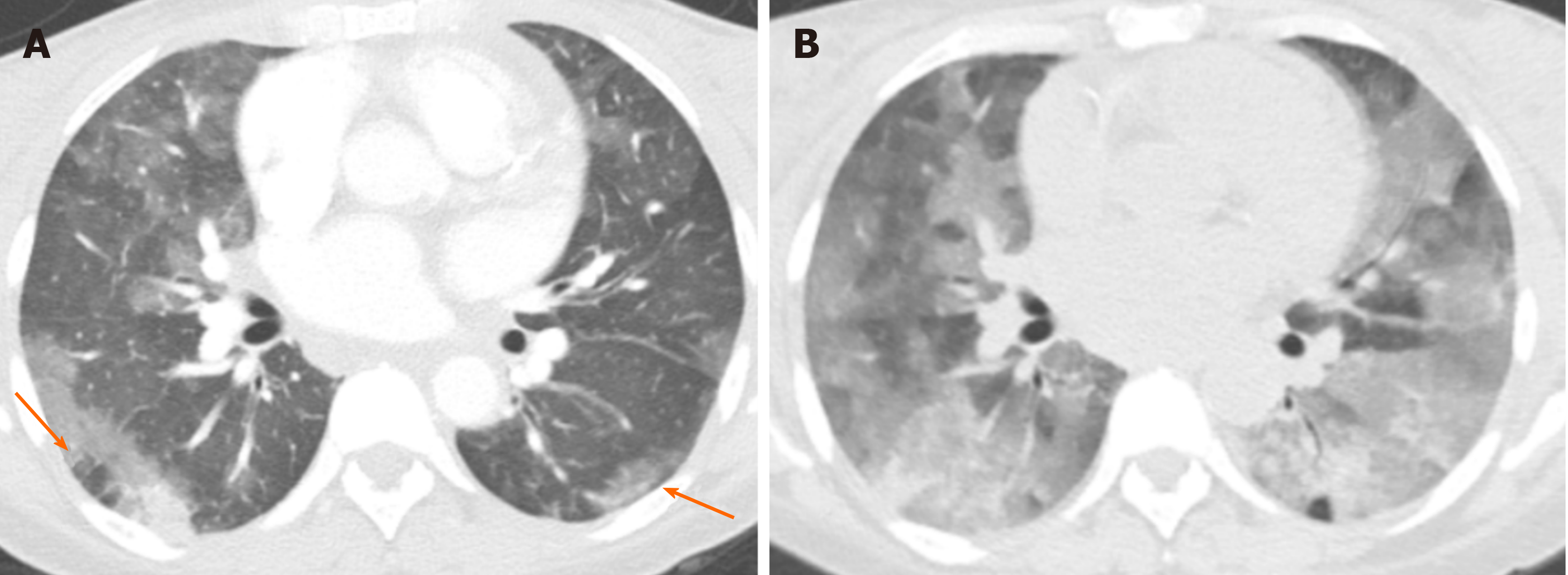
Chronic Airspace Disease Review Of The Causes And Key Computed Tomography Findings

Figure 2 From Tree In Bud Pattern Semantic Scholar

Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease And Its Mimics Thoracic Key

Signs And Findings In Infection Lungs

Figure 2 From Tree In Bud Pattern Semantic Scholar
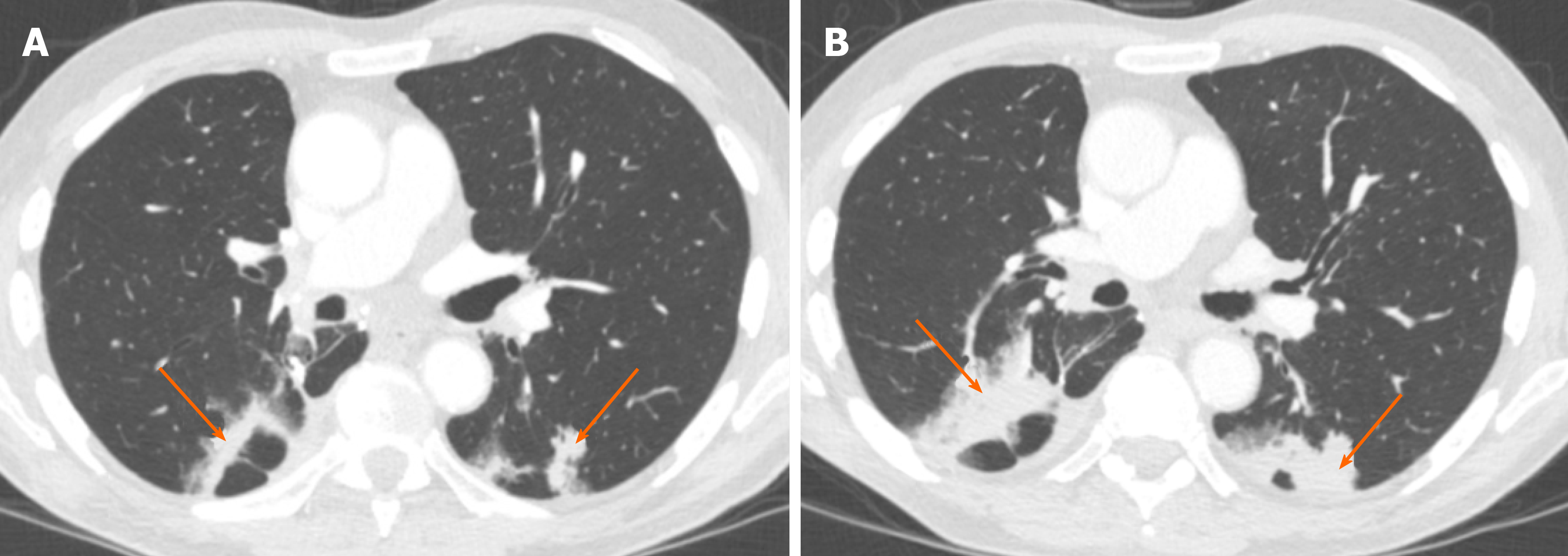
Chronic Airspace Disease Review Of The Causes And Key Computed Tomography Findings

Figure 2 From Tree In Bud Pattern Semantic Scholar

Ct Scan Showing Cavitary Lesion In The Right Lung And Tree In Bud Sign Download Scientific Diagram
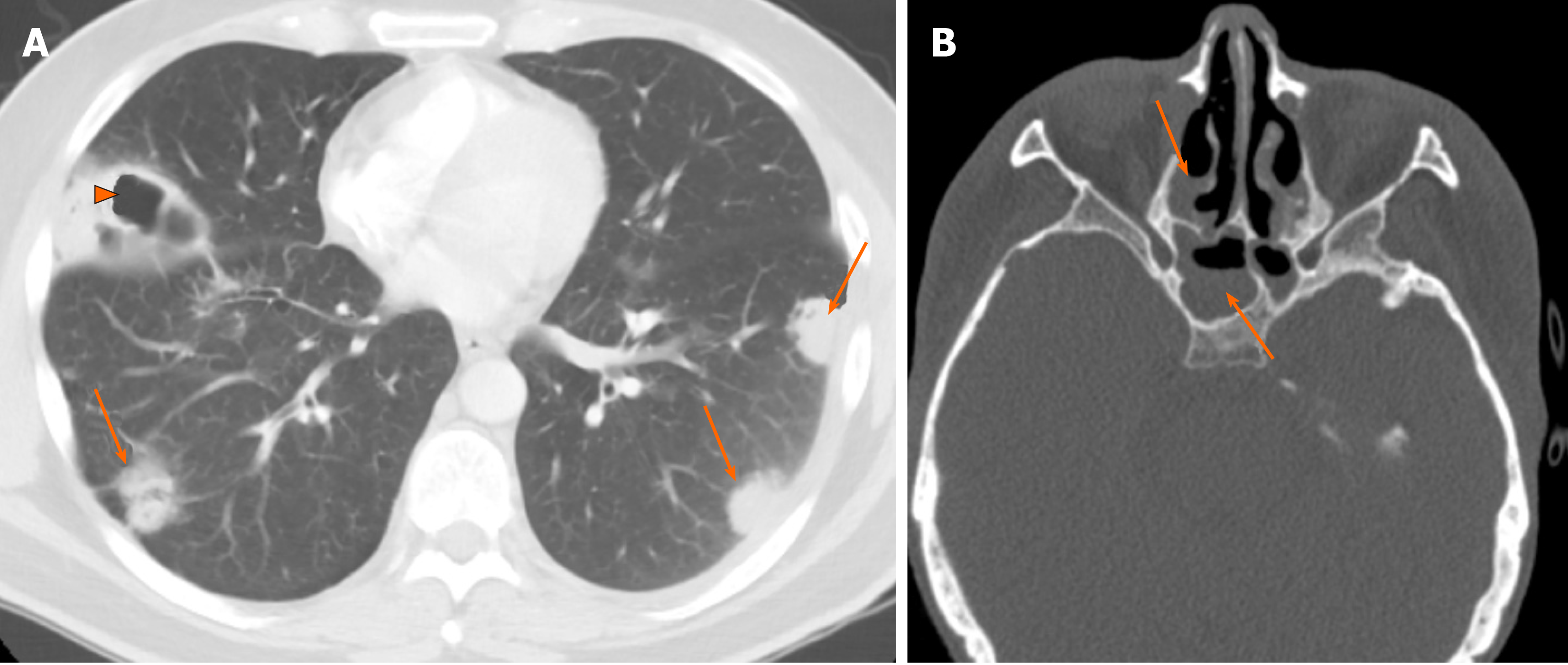
Chronic Airspace Disease Review Of The Causes And Key Computed Tomography Findings
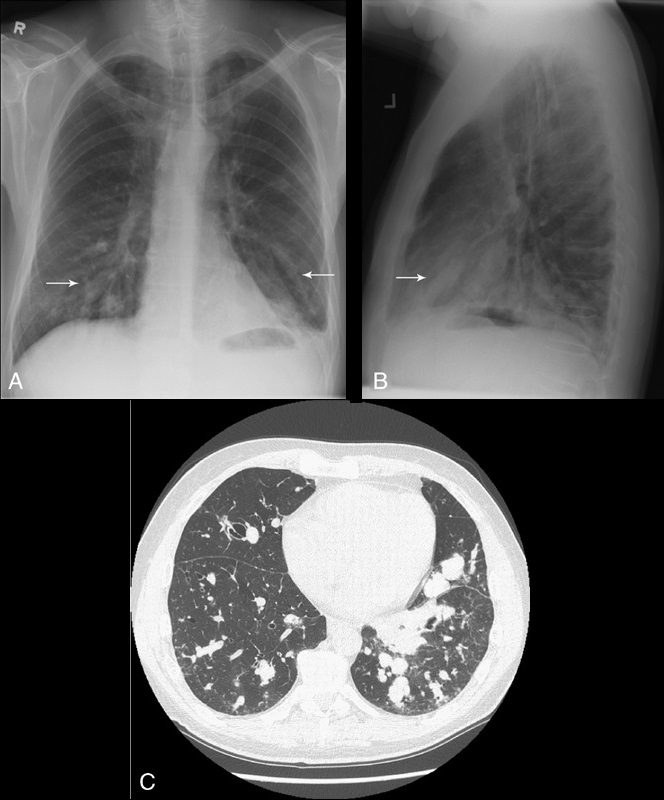
Signs And Findings In Infection Lungs

Ground Glass Opacification Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Clinical Characteristics And Ct Manifestations Of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis In Hospitalised Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Clinical Radiology